Get access to all handy features included in the IVIS website
- Get unlimited access to books, proceedings and journals.
- Get access to a global catalogue of meetings, on-site and online courses, webinars and educational videos.
- Bookmark your favorite articles in My Library for future reading.
- Save future meetings and courses in My Calendar and My e-Learning.
- Ask authors questions and read what others have to say.
The expression of Parathyroid hormone-related peptide and Indian hedgehog in intervertebral disc degeneration
de Rooij K.M., Bach F.C...
Get access to all handy features included in the IVIS website
- Get unlimited access to books, proceedings and journals.
- Get access to a global catalogue of meetings, on-site and online courses, webinars and educational videos.
- Bookmark your favorite articles in My Library for future reading.
- Save future meetings and courses in My Calendar and My e-Learning.
- Ask authors questions and read what others have to say.
Read
Introduction
Intervertebral disc (IVD) degeneration is common in dogs and humans and associated with back pain (1). During IVD degeneration, the water content decreases in the center of the IVD, the nucleus pulposus (NP), resulting in a low shock absorption capacity of the IVD (2,3). Current treatments reduce pain rather than repair the IVD(1). In order to achieve functional repair with the aid of regenerative agents, further knowledge of the pathogenesis of IVD degeneration and the pathways involved is required. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the unexplored role of Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) and Indian hedgehog (IHH), which play a role in cartilage homeostasis and degeneration (e.g. osteoarthritis), in the IVD.

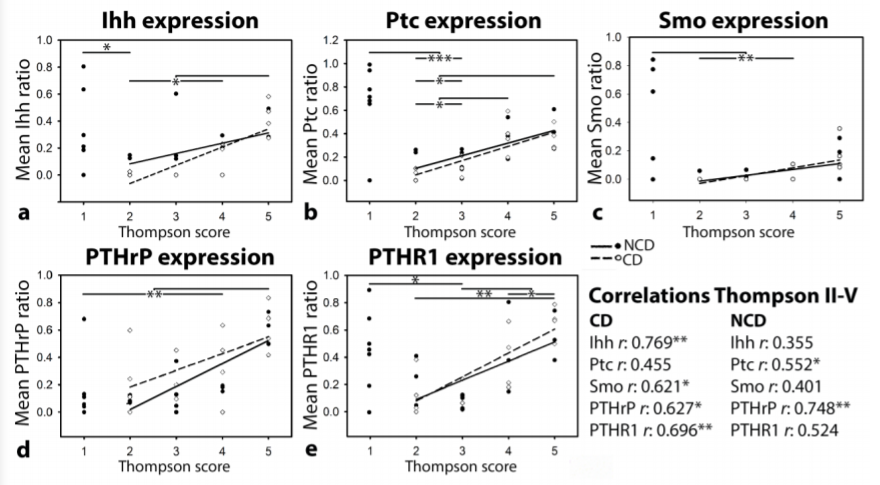
Figure 1. The protein expression of Parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP), PTHrP receptor 1 (PTHR1), Indian hedgehog (IHH), and the IHH receptors Patched (Ptc) and Smoothened (Smo) in canine intervertebral discs with different degeneration graes. * P<0,05; ** p<0,01; *** P<0,001; CD: chondrodystrophic dog breeds; NCD: non-chondrodystrophic dog breeds.
Materials and methods
Protein expression of PTHrP, PTHR1 (PTHrP receptor 1), IHH, Ptc (Patched: IHH receptor), and Smo (Smoothened: transmembrane protein that activates downstream hedgehog signaling) was determined by immunohistochemistry in canine (n= 7 or 8 per Thompson grade) and human IVDs (n= 4 or 5 per Thompson grade) with different degeneration scores, ranging from healthy (grade I) to severely degenerated (grade V). The mean positive cell ratio per Thompson grade was assessed per IVD.
Results
Generally, PTHrP and IHH (receptor) expression decreased from healthy to early degenerated IVDs and increased from early to severely degenerated IVDs in dogs (Figure 1) and humans. To investigate the exact role of PTHrP and IHH in healthy and degenerated IVDs, IVD cells are currently being cultured with or without PTHrP and IHH in vitro.
Conclusion
PTHrP and IHH expression increased during canine and human IVD degeneration, indicating that IHH and PTHrP signaling is active in healthy and degenerated IVDs. Thus, PTHrP and IHH might play a role in IVD degeneration or regeneration. It remains to be determined whether they serve as a therapeutic approach to prevent or delay IVD degeneration.
References
- Bach F, Willems N, Penning L, Ito K, Meij B, Tryfonidou M. Potential regenerative treatment strategies for intervertebral disc degeneration in dogs. BMC Vet Res 2014;10:3-3.
- Bergknut N, Smolders L, Grinwis GCM, Hagman R, Lagerstedt A, Hazewinkel HAW, et al. Intervertebral disc degeneration in the dog. Part 1: Anatomy and physiology of the intervertebral disc and characteristics of intervertebral disc degeneration. Vet J 2013;195(3):282-291.
- Priyadarshani P, Li Y, Yao L. Advances in biological therapy for nucleus pulposus regeneration. Osteoarthr Cartil 2016;24(2):206-212.
Get access to all handy features included in the IVIS website
- Get unlimited access to books, proceedings and journals.
- Get access to a global catalogue of meetings, on-site and online courses, webinars and educational videos.
- Bookmark your favorite articles in My Library for future reading.
- Save future meetings and courses in My Calendar and My e-Learning.
- Ask authors questions and read what others have to say.


Comments (0)
Ask the author
0 comments